In the fast-paced world of technological advancements, artificial intelligence (AI) is playing a pivotal role in scientific transformation. Recently, Google introduced C2S-Scale, a 27-billion-parameter model built on the Gemma family, unveiling a groundbreaking discovery in cancer treatment. Developed in collaboration with Yale University, this model can interpret the molecular language of human cells and propose a novel hypothesis for treating “cold” tumors — a concept previously absent from scientific literature.
Announced in October 2025, this breakthrough highlights AI’s potential to generate new scientific knowledge. In this article, we dive deep into the details of this advancement, its implications for cancer therapy, and the future of AI in medicine. If you’re looking for accurate, reliable insights into AI and cancer research, keep reading.
What Is C2S-Scale and How Does It Work?
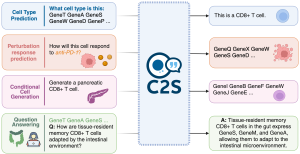
C2S-Scale (Cell2Sentence-Scale) is a large language model (LLM) built upon Google’s open-source Gemma models. Trained on massive biological datasets, it interprets cellular behavior — gene expression patterns, molecular interactions, and immune responses — as if they were sentences in a language.
– Scale & Compute Power: With 27 billion parameters, the model runs on high-performance GPUs and processes complex cellular data at scale.
– Scientific Collaboration: A joint effort between Google DeepMind and Yale University, combining expertise in AI and biology.
– Core Application: Focused on understanding how “cold” tumors evade the immune system — one of the biggest challenges in cancer immunotherapy.
Unlike traditional tools that merely analyze data, C2S-Scale generates innovative hypotheses, setting it apart in biomedical research.
The Breakthrough: Silmitasertib’s Role in Cancer Therapy
The most exciting outcome of C2S-Scale is its prediction about silmitasertib (CX-4945), a drug previously studied in clinical trials for various cancers. When combined with low-dose interferon, this drug can turn “cold” tumors “hot” — making them visible and vulnerable to the immune system.
– How the Discovery Happened: The model simulated over 4,000 candidate drugs under different conditions and predicted silmitasertib could amplify immune signaling.
– Lab Validation: In vitro experiments confirmed the hypothesis. The drug-interferon combo increased tumor antigen recognition by the immune system by up to 50%.
– Impact on Patients: Cold tumors are often resistant to immunotherapy. This new approach could open doors to more effective treatments for breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers.
This discovery is entirely novel — with no prior mention in existing research — proving AI’s ability to create original scientific insights.
Why This Matters for Science and Medicine
This milestone marks a turning point in AI-driven science. Google emphasizes that C2S-Scale isn’t just an analysis tool — it’s a hypothesis generator capable of producing experimentally valid ideas.
– Boost to Immunotherapy: By enhancing immune response, this method could significantly improve cancer treatment success rates.
– Future of AI in Biology: Models like this can accelerate drug discovery and reduce research costs.
– Next Steps & Challenges: While early results are promising, clinical trials are needed to confirm safety and efficacy in humans.
According to official reports from Google and Yale, this advancement could usher in a new era of AI-powered medicine.
Conclusion: AI Is the Future of Cancer Treatment
Google’s C2S-Scale proves that artificial intelligence is no longer just a support tool — it’s a true partner in scientific discovery. By unlocking new ways to treat resistant tumors, this breakthrough brings fresh hope to millions of cancer patients worldwide.
Stay updated with the latest in AI and medical innovation by following trusted sources like the Google Research Blog and peer-reviewed journals.


